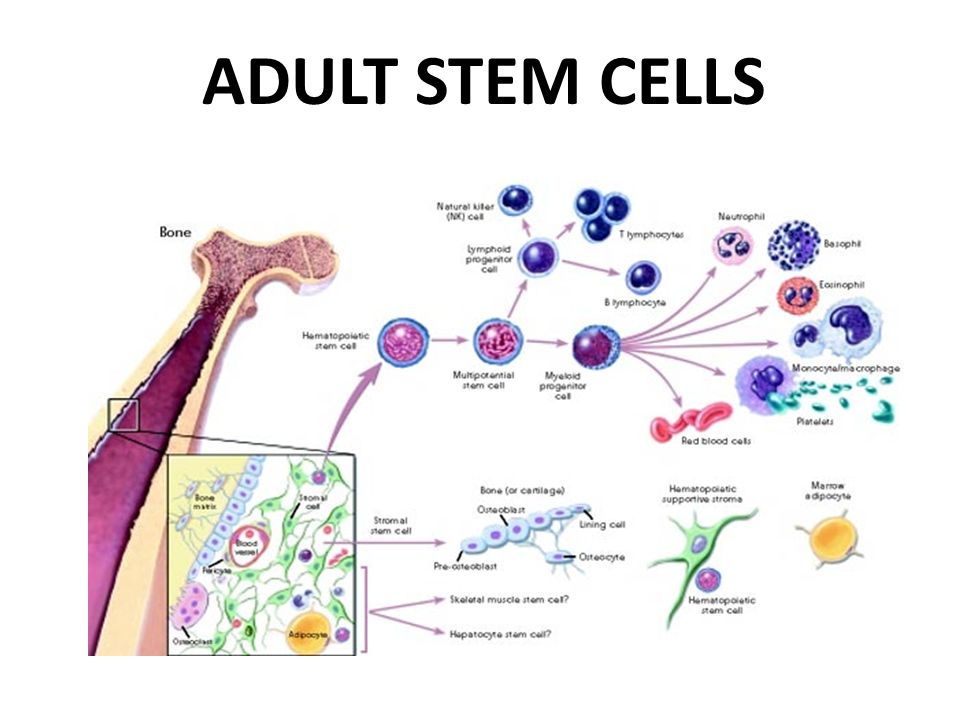
Adult Embryonic Stem Cell
Human embryonic stem cell research has been promoted as being the best way to pursue cell-based therapies for a number of diseases. Although embryonic stem cells are the most versatile type of stem cells, they are unacceptable for therapy because they spontaneously form tumors when transplanted into a compatible host
Benefits of Stem Cells to Human Patients Adult Stem Cells v. Embryonic Stem Cells Download This List Peer-Reviewed References (not a complete listing, sample references) Adult Stem Cells Embryonic Stem Cells Cancers: Brain Cancer Retinoblastoma Ovarian Cancer Skin Cancer: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Testicular Cancer Tumors

Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from adult cells. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka’s lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes encoding transcription factors could convert adult

Adult Stem Cell Treatment is a natural solution to treat a variety of medical diseases and conditions. Learn about it’s positive impact on our site.
Can Stem Cell Plant-Based be an Alternative to Embryonic Stem Cell? If you’re looking for an alternative to embryonic stem cell, a new powerful plant based stem cell nutrition has been documented to support the release of 4.5 to 6 million of adult stem cells from the bone marrow into circulation after taking 2 capsules.
Search for articles by this author Affiliations. Department of Stem Cell Biology, Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8507, Japan
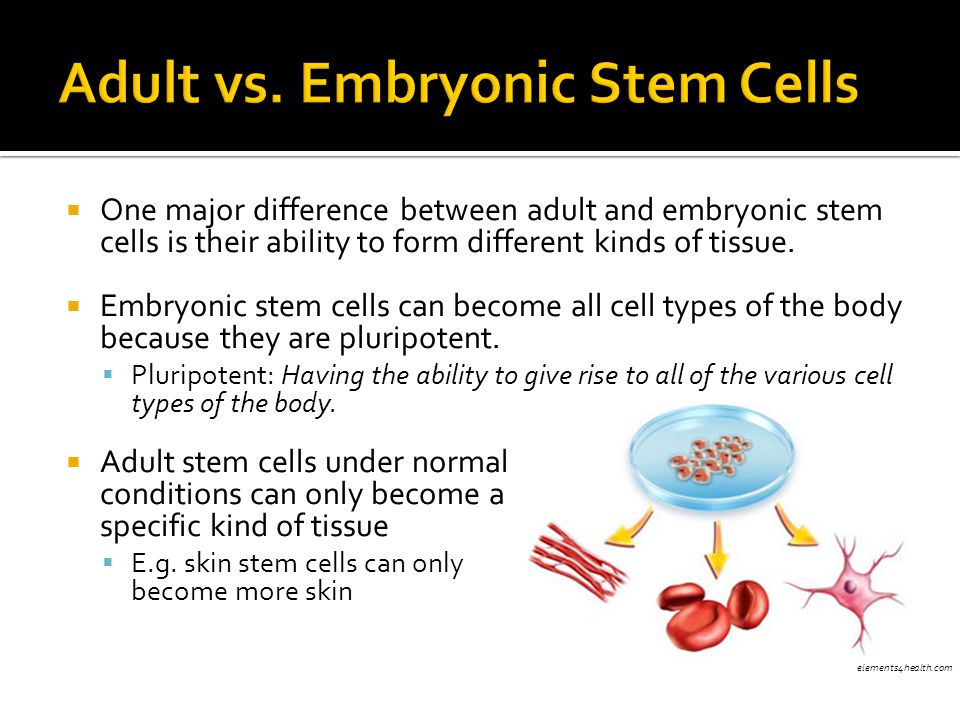
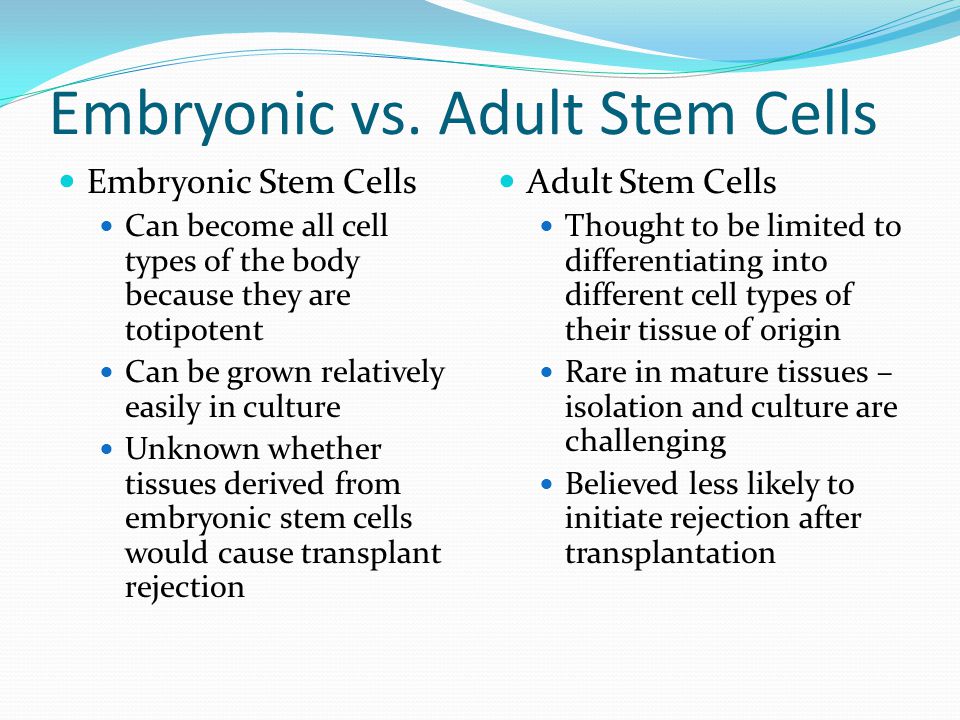
Potency specifies the differentiation potential (the potential to differentiate into different cell types) of the stem cell.. Totipotent (a.k.a. omnipotent) stem cells can differentiate into embryonic and extraembryonic cell types.

Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors

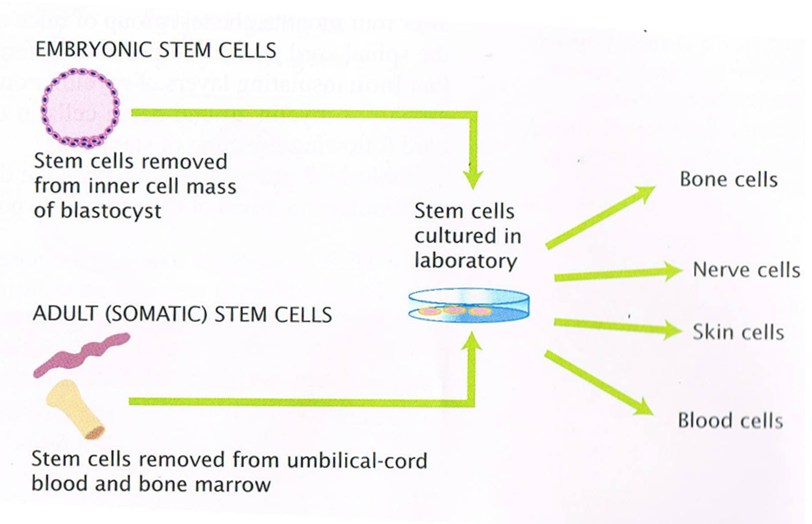

This is a part of Potent Biology: Stem Cells, Cloning, and Regeneration The inner cell mass (ICM) cells of blastocyst-stage early human embryos can be removed and cultured. These cells can be grown in the lab indefinitely. Various growth factors cause these cells to develop into a variety of

Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors