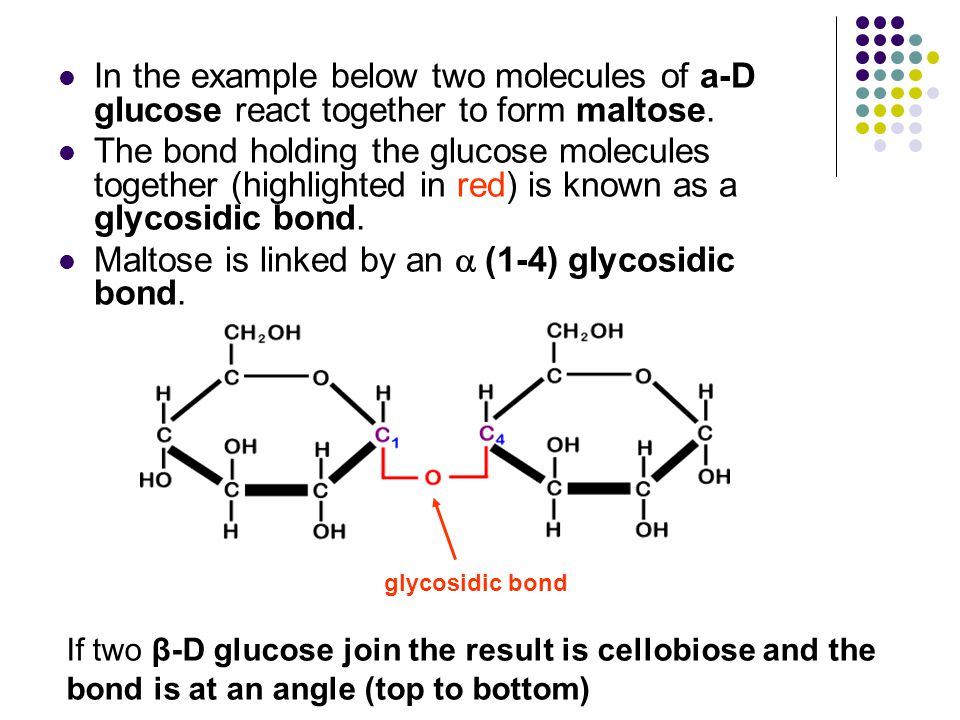
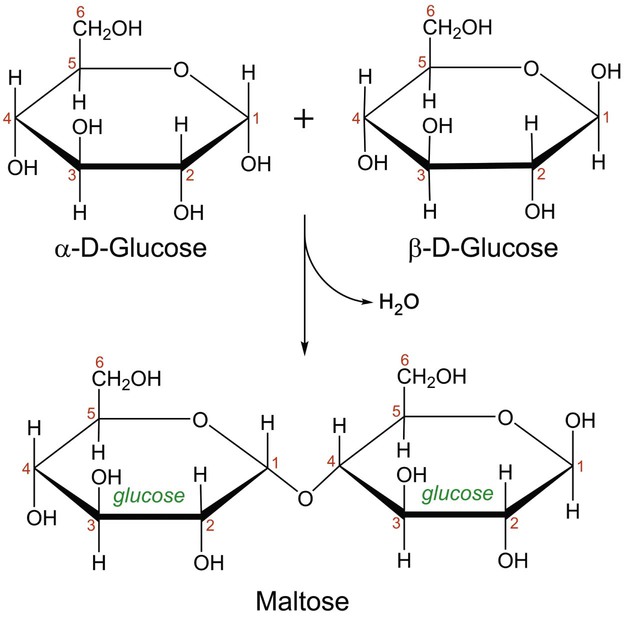
Maltose And Water React To Form Two Molecules Of Glucose In What Process

Types. Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both substance and water molecule to split into two parts.
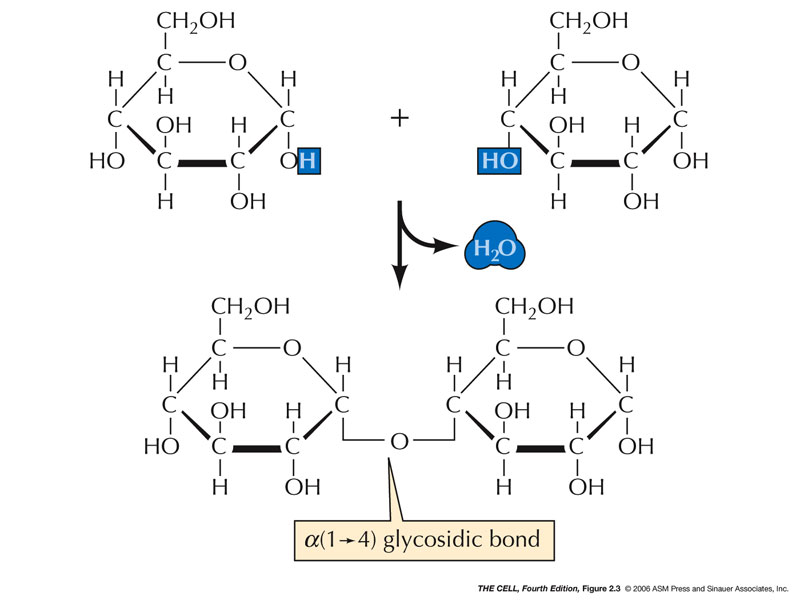
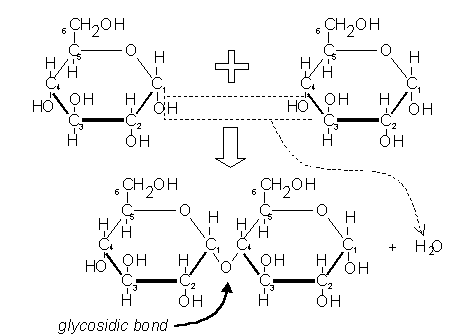
Condensation is a chemical process by which 2 molecules are joined together to make a larger, more complex, molecule, with the loss of water. It is the basis for the synthesis of all the important biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) from their simpler sub-units.
Dehydration or condensation reactions. (When monomers are linked together to form a more complex polymer, a water molecule is removed by …
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6.Glucose circulates in the blood of s as blood sugar.It is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
Deciding what foods to buy was simpler when most food came from farms. Now, factory-made foods have made chemical additives a significant part of our diet.
Flours contain a lot of nutrients such as saccharides, protein and fat. The human body is capable of breaking down food and during this process energy is released.
Free radicals combine quickly with molecules such as fats, proteins, and DNA, converting them into free radicals and triggering chain reactions that destroy still more molecules.
Glycogen, Starch and Inulin are storage polysaccharides. 1) Glycogen . Glycogen is a readily mobilized storage form of glucose. It is a very large, branched polymer of glucose residues (Figure-1) that can be broken down to yield glucose molecules when energy is needed.
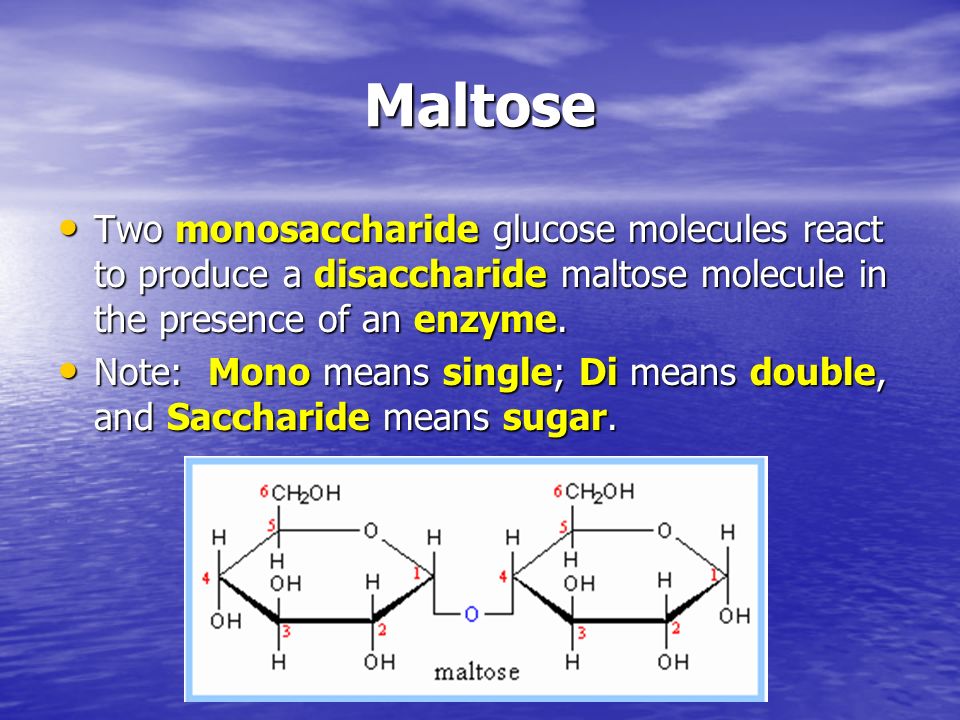
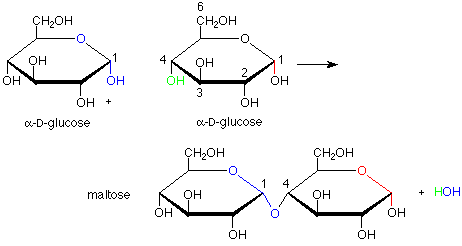



Carbohydrates . Carbohydrates (also called saccharides) are molecular compounds made from just three elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) and disaccharides (e.g. sucrose) are relatively small molecules.
Water molecules attract each other due to a phenomenon called polarisation (water is said to be a polar molecule):. one region of the molecule is on average, at any one time, more negatively charged than the opposite region