What S The Difference Between Sex And Gender
What’s the difference between being transgender or transsexual and having an intersex condition?
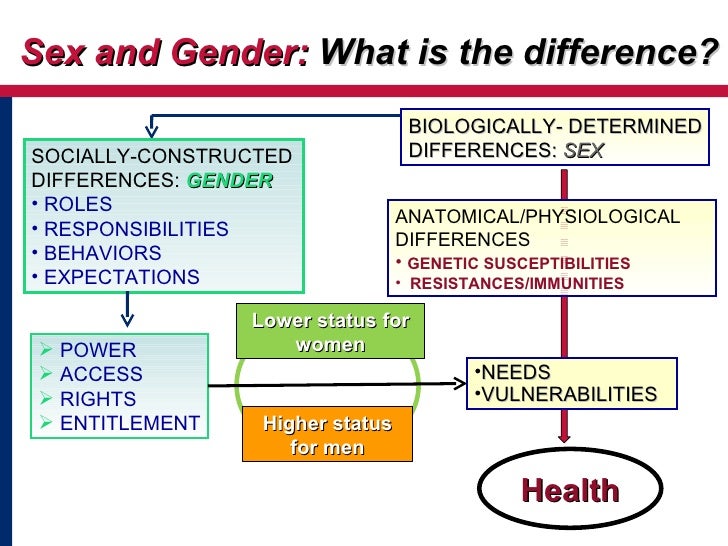
How do you know when to call something a sex difference rather than a gender difference? Using the definitions given for sex (biological differences between males and females) and gender (socially defined differences between men and women), sex differences therefore refer only to those differences that can be attributed solely to …

Gender and sex (sexuality) are two words that are used quite often in place of each other. It is common to find blanks in forms asking you for your sex or gender and your response in both the cases would be the same.

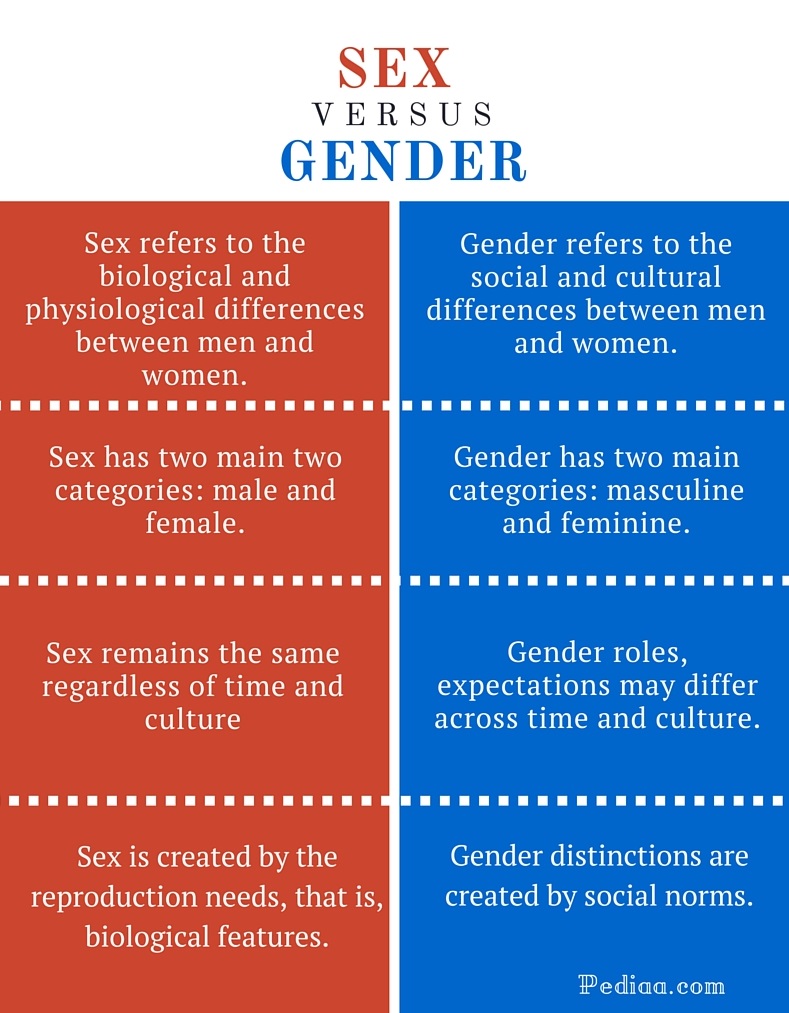
Sex = male and female Gender = masculine and feminine So in essence: Sex refers to biological differences; chromosomes, hormonal profiles, internal and external sex organs.
The distinction between sex and gender differentiates a person’s biological sex (the anatomy of an individual’s reproductive system, and secondary sex characteristics) from that person’s gender, which can refer to either social roles based on the sex of the person (gender role) or personal identification of one’s own gender based on an …
Sex is the actual genitalia you are born with, and that classifies you as male or female. Gender may be more your internal identity and the role you play in life.
It’s a common misconception that a person’s gender identity and sexual orientation are connected, but they are not

When Facebook added 50 gender options for its billions of users, some people wondered: What is the difference between transsexual and transgender?


There is some overlap when defining bisexual and pansexual orientation; however, there are important differences between the two identities. Bisexual people are attracted sexually and romantically to both males and females, and are capable of engaging in sensual relationships with either sex


Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to, and differentiating between, masculinity and femininity.Depending on the context, these characteristics may include biological sex (i.e., the state of being male, female, or an intersex variation), sex-based social structures (i.e., gender roles), or gender identity.